Overhead Fuse Cutout: A Critical Component in Distribution Systems
An overhead fuse cutout is a key protective device. It’s widely used in electrical distribution networks, and it usually works for voltages up to 38 kV. Its main job is to safely stop fault currents. This way, it isolates the faulty part of the circuit and keeps the rest of the system working. It also acts as an important protection for distribution transformers, capacitors, and feeders.
A standard cutout has three main parts. These are a waterproof insulating holder (you can also call it the body), a fuse carrier, and the fuse element. The holder is often made of porcelain or polymer. It gives both insulation and mechanical support. The fuse carrier holds the fusible element. It’s made to pivot and drop down clearly when the fuse works. This “drop-out” feature lets people see there’s a fault clearly. It helps line crews find the problem fast.
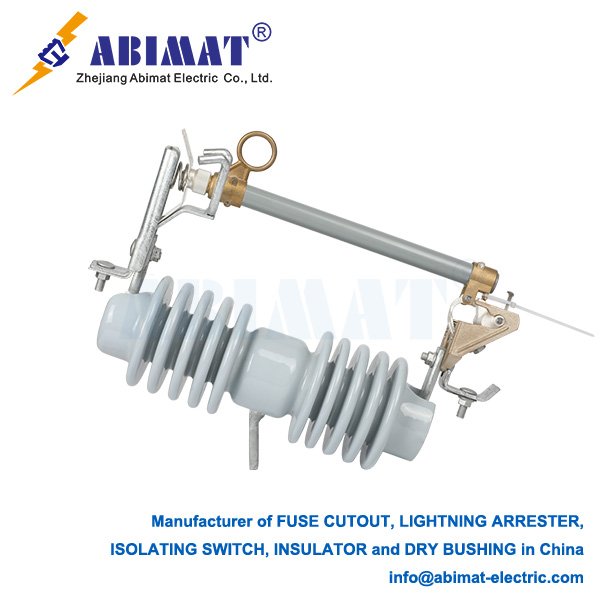
It works in a simple way, but it’s very effective. When the load is normal, current flows through the fuse element without stopping. If there’s a steady overcurrent or a short-circuit, the fusible link melts. It also creates an arc. The cutout is made to put out this arc well. It usually uses de-ionizing filler material inside the fuse tube. When the arc is put out and the circuit is broken, the fuse carrier lets go. It drops open too, and this gives full isolation.
The fuse cutout has key benefits. These are its simplicity, reliability, and low cost. It doesn’t need an external power source to work. That makes it a fully passive and fail-safe device. It shows problems visually, and this makes finding faults and fixing the system faster.
To sum up, Abimat the overhead fuse cutout is still a basic and reliable device. It’s used for overcurrent protection in overhead distribution lines. Its tested design works well to balance important needs. These needs are safety, system reliability, and operational efficiency.


